Turn animal co-products into high-value ingredients
According to The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), 35% of the world’s harvest of fisheries and aquaculture is either lost or wasted. There is a huge opportunity to turn this waste into a protein source.
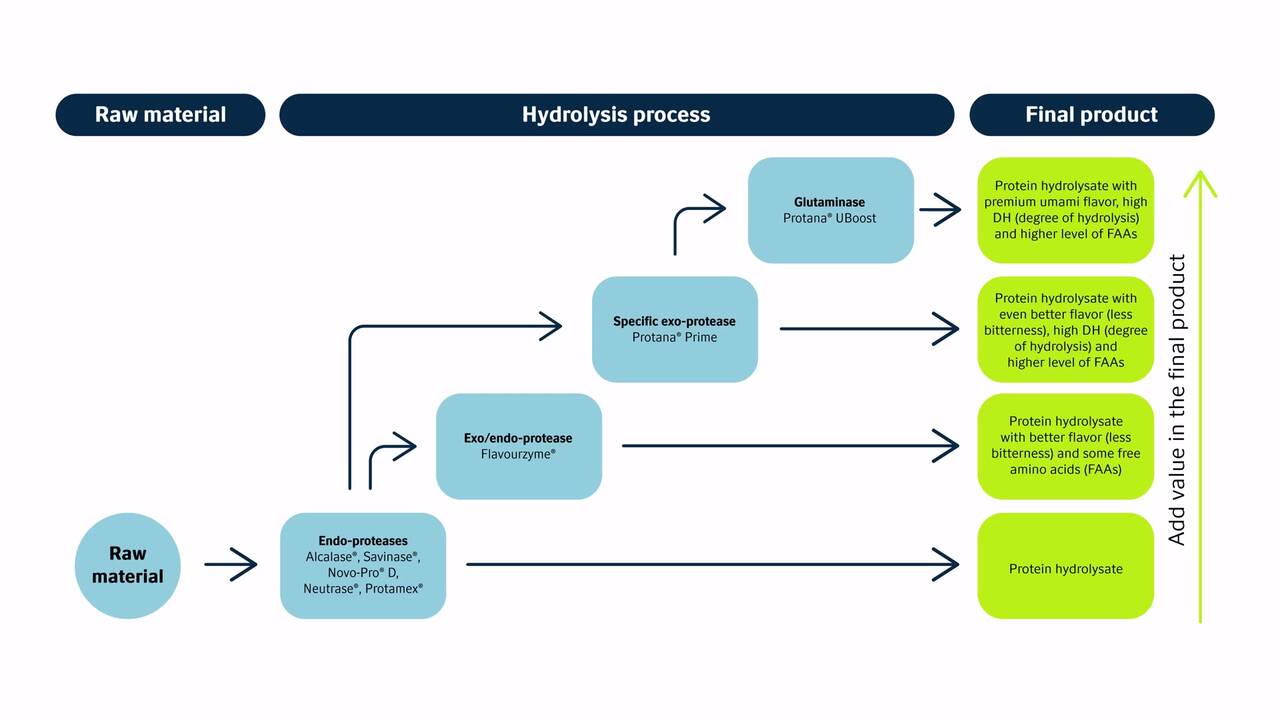
Enzymes are environmentally friendly processing aids. They convert animal by-products and/or co-products into valuable protein sources. Enzymatic protein hydrolysis solubilizes meat co-products by converting them into protein hydrolysates. These are proteins that have been at least partially broken down into small peptides and amino acids.